Where Is the Endpoint of a Titration Curve
V A and V B are the volumes of the acid and base respectively. A AEAVAV Figure 11-6.
9 1 Overview Of Titrimetry Chemistry Libretexts
The endpoint mode represents the classical titration procedure.

. At this point moles of NH added moles of HCl in the analyte. This is the pH recorded at a time point just before complete neutralization takes place. This sort of plot is called a linear titration curve.
In a titration the equivalence point is the point at which exactly the same number of moles of hydroxide ions have been added as there are moles of hydrogen ions. In a nutshell Endpoint is the point in the titration process where the indicator changes its color whereas the equivalence point indicates the completion of the reaction between titrant. In real life we dont often know the moles of analyte- were doing the titration.
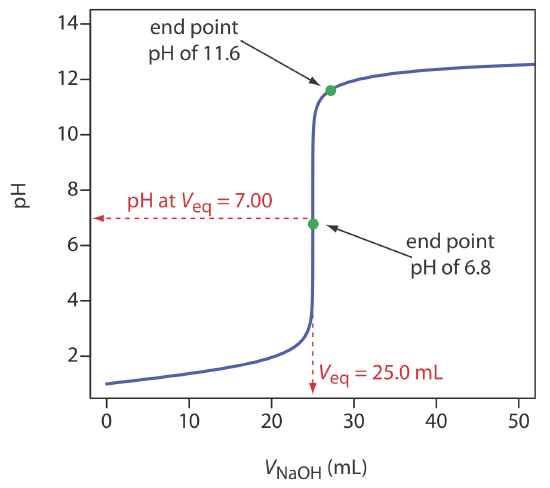
Pg334 The end point in a potentiometric titration can be determined by one of the following three methods Direct plot first-derivative curve and second-derivative curve. M A is the molarity of the acid while M B is the molarity of the base. The curve shows the same trend as a weak acid titration where the pH does not change for a while spikes up and levels off again.
Endpoint titration mode EP. You can either calculate the volume that has been used to titrate or know when the titration is done. Diagram of solution transformation as titration begins.
A titration will usually generate a characteristic titration curve from a plot of pH vs. Below is a titration curve for the titration of a strong acid with a strong base. Titration Curve Equivalence Point.
The end point is where the titration ends in practice. In a titration if the base is added from the burette and the acid has been accurately measured into a flask. Up to 24 cash back A titration curve is a graph of the pH changes that occur during an acid- base titration versus the volume of acid or base added.
YOUR QUESTION IS UNCLEAR. It is based on the assumption that end point detection should be in the 01 range of the equivalence point. The equivalence point is the end of a titration where the stoichiometry of the reaction is exactly satisfied or moles H moles OH-.
50 Calculation and Reporting a. The term given to the color change of an indicator when an acid and base react. With an automatic titrator the sample is titrated until a predefined value is reached eg.
A plot showing the change in pH of the solution in the conical flask as the titrant is added from the burette to the analyte. Like other titration terms such as titrants analyte burette and pipette endpoint and equivalence points are equally important in fully understanding the titration technique. The titrant is added until the end of the reaction is observed eg by a colour change of an indicator.
The end point is the maximum of the first derivative AEAV or the zero crossing of the second derivative. M A V A M B V B. You want to measure the volumes at the endpoint of the titration when the acid and base have neutralized each other.
L Construct the titration curve by plotting the pH readings on the ordinate y-axis against the titrant volume added on the abscissa x-axis. The pH of the solution is recorded upon the addition of a small amount of titrant. Answer 1 of 3.
In an acidbase titration the. The acid or base in. However very often we can easily spot a point very close to the equivalence point - and thats where the end point will be.
Volume of titrant added. A titration curve is a curve in graph the x-coordinate of which represents the volume of titrant added since the beginning of the titration and the y-coordinate of which represents the concentration of the analyte at the corresponding stage of the titration in an acidbase titration the y-coordinate usually represents the pH of the solution. Find and report the total alkalinity endpoint as the pH of the bicarbonate equivalence point the inflection point.
The end point refers to when an indicator changes color and HInd Ind-. The difference occurs when the second acid reaction is taking place. The same curve happens again where a slow change in pH is followed by a spike and leveling off.
This is the equivalence point halfway up the steep curve. Titration calculations generally involve this equation. What is End Point in Titration.
Based on the pH an acid-base indicator eg phenolphthalein switches colour. What do you mean CALCULATE the titration endpoint. Calculate titration parameter be it pH pMe or redox potential for 999 and 1001 titration percentage and select indicator that.
You should first take acid or base in a beaker to titrateThen you should add indicatorAfter tha. The key distinction between equivalence and endpoint is that the point of equivalence is a point where the chemical reaction comes to an end while the endpoint is the point in a procedure where the colour transition takes place. The X-intercept on a plot with moles of analyte on the Y-axis and volume of titrant added on the X-axis will be the endpoint.
The closer the end point to the equivalence point the better but it is often not easy to find a good method of equivalence point detection.

No comments for "Where Is the Endpoint of a Titration Curve"
Post a Comment